Astronomer's New Repo - Cosmos (ENG)
Astronomer’s Brand New Repo - Cosmos
Astronomer, a company that built Airflow released a new repo - Cosmos.
Cosmos is a framework that can automatically generate Airflow DAGs from other tools/frameworks. Currently, it only supports dbt, but Cosmos is planning to support notebook IDE like Jupyter and Hex.
So what does this Cosmos mean? Why is it so amazing (at least for me)?
Since dbt is not a scheudling tool, you need some other scheduling tool (most likely Airflow) to consistently run and manage the model.
However, integrating dbt and Airflow was definitely not an easy task.
You can either:
- Use bash operator and run ‘dbt run’ in command
- Just use dbt cloud and use dbt cloud provider
- (Not guided in dbt blog..but..) Create your own dbt operator, and create a task that can extract from dbt manifests and generate graph info of dbt node
Definitely, all three are not welcomed.
- This will have almost no observability, and bash operator is too naive.
- This solution is not an ideal solution for dbt Core users.
- Yes, you can do this. But you need some good engineer inside your team.
Now, by using Cosmos, integration between dbt and Airflow is much much easier.
So how do we use Cosmos?
Simple. Just pip install it like following:
pip install astronomer-cosmos[dbt-all]
Then, you can just use (thanks to the Cosmos example):
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow import DAG
from airflow.operators.empty import EmptyOperator
from cosmos.providers.dbt.task_group import DbtTaskGroup
with DAG(
dag_id="extract_dag",
start_date=datetime(2023, 3, 24),
schedule="@daily",
) as dag:
start = EmptyOperator(task_id="ingestion_workflow")
dbt_tg = DbtTaskGroup(
group_id="dbt_tg",
dbt_project_name="chan_example",
conn_id="airflow_db",
dbt_args={
"schema": "public",
},
)
end = EmptyOperator(task_id="some_extraction")
start >> dbt_tg >> end
By this code, a task group inside dbt project will be rendered like below.
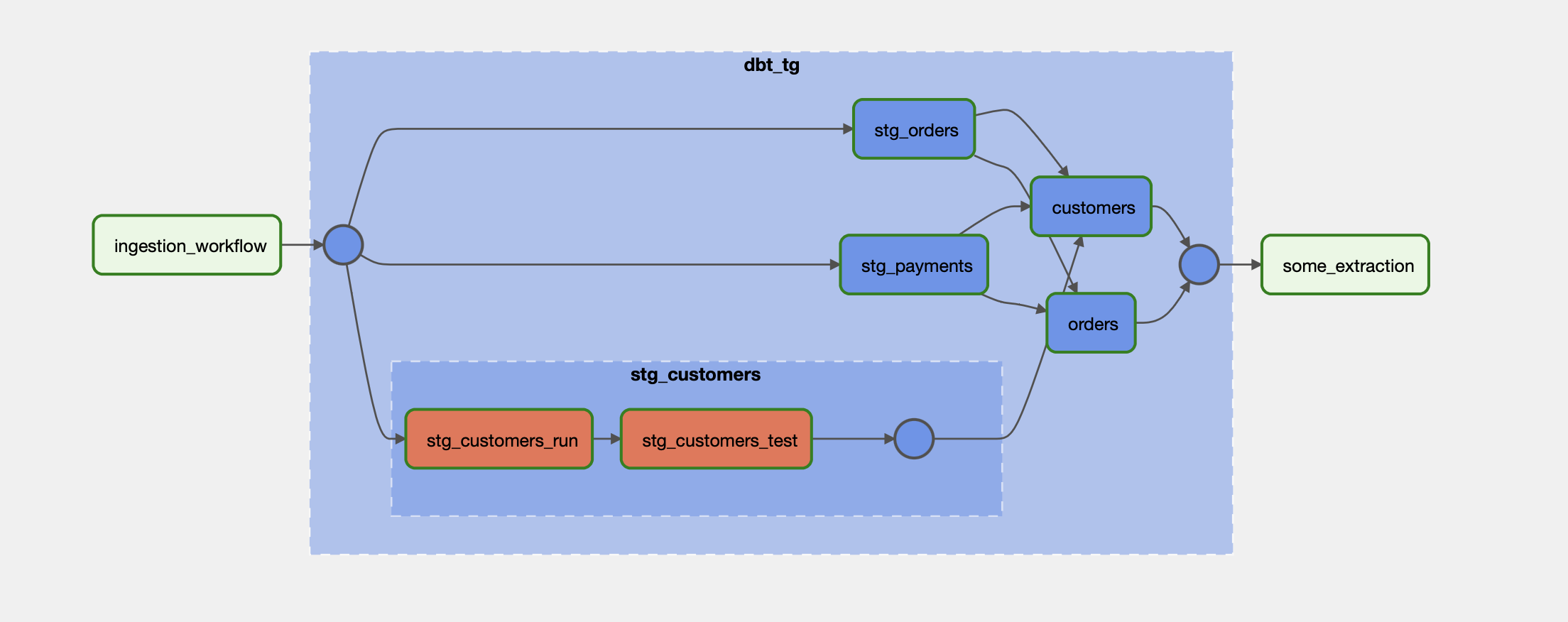
So let us deep dive into Cosmos.
- First, you should dbt root path and model directory. You can override
dbt_root_pathanddbt_models_dirto configure your own directory instead of default configuration (root path:/usr/local/airflow/dbt, model:models) - Cosmos provides two ways for dbt to be rendered. First is
cosmos.providers.dbt.DbtDagclass which creates a single and full DAG for dbt project. Second iscosmos.providers.dbt.DbtTaskGroupclass which renders as a task group inside DAG. By using task group, you can include other tasks before and after dbt project task group. - Cosmos currently provides connections to bigquery, databricks, postgres, redshift and snowflake. You can either provide
conn_idwhich will use Airflow connection, or you can provide dbt_args. This let engineers to be freed from managing separate profiles.yml. However, currently most connections are based on user/password authentication. - For scheduling, you can use time-based scheduling my providing
schedule interval. You can also use data-aware scheduling. By providing dataset in schedule, you can let following dag to run after completion of preceding dag. For example,schedule=[get_dbt_dataset("my_conn", "project_one", "my_model")]If you provide this schedule inside project_two DAG, this will run immediately after project_one. - You can add test after each model. This can be configured by
test_behaviorvariable. - You can filter model by providing
selectandexcludeparameter. For example, you can provide something like: select={“configs”: [‘tags:daily’]}. You can also filter by path.
Thanks to Comsos, now we can integrate dbt easily. But still, Cosmos needs more development. For example, there are only five operators right now in Cosmos: DbtRunOperator, DbtTestOperator, DbtLSOperator, DbtSeedOperator, and DbtRunOperationOperator. There can be more operators like DbtSnapshotOperator. Also, authentication and connection variety is still limited.
But one thing is clear: dbt and Airflow is getting closer and both of them are clearly definite Modern Data Stack (MDS).
Reference
https://www.getdbt.com/blog/dbt-airflow/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MhCuxTDlVkE
https://astronomer.github.io/astronomer-cosmos/